New to Kubepack? Please start here.
Scenario-11
This doc explains how pack up command works and how install.sh file is generated.
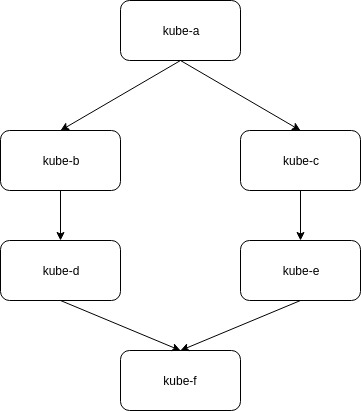
To learn how this works, clone this repository and checkout branch test-11. You will find dependency-list.yaml file in the project root.
$ cat dependency-list.yaml
items:
- package: github.com/kubepack/kube-b
branch: test-11
- package: github.com/kubepack/kube-c
branch: test-11
Now, run pack up -f . command in this project root. This executes the following steps.
- Combines
manifests/vendorandmanifests/patchtomanifests/outputfolder. - Generates a DAG(Directed Acyclic Graph) from
dependency-list.yaml. From this dependency graph, it generates ainstall.shfile. This installer script contains commands to deploymanifests/outputfolder. Each parent package can provide their owninstall.shscript. If no script is provided,kubectl apply -R -f .command will be used to install a package.
This is what the auto-generated installer script looks like:
cat manifests/output/install.sh
#!/bin/bash
pushd manifests/output/github.com/kubepack/kube-f
kubectl apply -R -f .
popd
pushd manifests/output/github.com/kubepack/kube-e
kubectl apply -R -f .
popd
pushd manifests/output/github.com/kubepack/kube-d
kubectl apply -R -f .
popd
pushd manifests/output/github.com/kubepack/kube-b
kubectl apply -R -f .
popd
pushd manifests/output/github.com/kubepack/kube-c
kubectl apply -R -f .
popd
pushd manifests/output/github.com/kubepack/kube-a
kubectl apply -R -f .
popd
- At first there will be
kubectl applycommand forkube-f, askube-fis independent in dependency chain. - After,
kube-f, there will bekube-eorkube-d. As, these two is least dependent afterkube-f. - Then,
kube-borkube-c, - At last
kube-aas this is most dependent repo.
If any repository’s manifests/app folder contain an install.sh file, then it will be used instead. Users can use their customize commands for deploy, these customize commands should be in manifests/app/install.sh file of that repository.